Review Classification using Active Learning
- Original Link : https://keras.io/examples/nlp/active_learning_review_classification/
- Last Checked at : 2024-11-21
Author: Darshan Deshpande
Date created: 2021/10/29
Last modified: 2024/05/08
Description: Demonstrating the advantages of active learning through review classification.
Introduction
With the growth of data-centric Machine Learning, Active Learning has grown in popularity amongst businesses and researchers. Active Learning seeks to progressively train ML models so that the resultant model requires lesser amount of training data to achieve competitive scores.
The structure of an Active Learning pipeline involves a classifier and an oracle. The oracle is an annotator that cleans, selects, labels the data, and feeds it to the model when required. The oracle is a trained individual or a group of individuals that ensure consistency in labeling of new data.
The process starts with annotating a small subset of the full dataset and training an initial model. The best model checkpoint is saved and then tested on a balanced test set. The test set must be carefully sampled because the full training process will be dependent on it. Once we have the initial evaluation scores, the oracle is tasked with labeling more samples; the number of data points to be sampled is usually determined by the business requirements. After that, the newly sampled data is added to the training set, and the training procedure repeats. This cycle continues until either an acceptable score is reached or some other business metric is met.
This tutorial provides a basic demonstration of how Active Learning works by demonstrating a ratio-based (least confidence) sampling strategy that results in lower overall false positive and negative rates when compared to a model trained on the entire dataset. This sampling falls under the domain of uncertainty sampling, in which new datasets are sampled based on the uncertainty that the model outputs for the corresponding label. In our example, we compare our model’s false positive and false negative rates and annotate the new data based on their ratio.
Some other sampling techniques include:
- Committee sampling: Using multiple models to vote for the best data points to be sampled
- Entropy reduction: Sampling according to an entropy threshold, selecting more of the samples that produce the highest entropy score.
- Minimum margin based sampling: Selects data points closest to the decision boundary
Importing required libraries
import os
os.environ["KERAS_BACKEND"] = "tensorflow" # @param ["tensorflow", "jax", "torch"]
import keras
from keras import ops
from keras import layers
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
import tensorflow as tf
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import re
import string
tfds.disable_progress_bar()Loading and preprocessing the data
We will be using the IMDB reviews dataset for our experiments. This dataset has 50,000 reviews in total, including training and testing splits. We will merge these splits and sample our own, balanced training, validation and testing sets.
dataset = tfds.load(
"imdb_reviews",
split="train + test",
as_supervised=True,
batch_size=-1,
shuffle_files=False,
)
reviews, labels = tfds.as_numpy(dataset)
print("Total examples:", reviews.shape[0])Result
Total examples: 50000Active learning starts with labeling a subset of data. For the ratio sampling technique that we will be using, we will need well-balanced training, validation and testing splits.
val_split = 2500
test_split = 2500
train_split = 7500
# Separating the negative and positive samples for manual stratification
x_positives, y_positives = reviews[labels == 1], labels[labels == 1]
x_negatives, y_negatives = reviews[labels == 0], labels[labels == 0]
# Creating training, validation and testing splits
x_val, y_val = (
tf.concat((x_positives[:val_split], x_negatives[:val_split]), 0),
tf.concat((y_positives[:val_split], y_negatives[:val_split]), 0),
)
x_test, y_test = (
tf.concat(
(
x_positives[val_split : val_split + test_split],
x_negatives[val_split : val_split + test_split],
),
0,
),
tf.concat(
(
y_positives[val_split : val_split + test_split],
y_negatives[val_split : val_split + test_split],
),
0,
),
)
x_train, y_train = (
tf.concat(
(
x_positives[val_split + test_split : val_split + test_split + train_split],
x_negatives[val_split + test_split : val_split + test_split + train_split],
),
0,
),
tf.concat(
(
y_positives[val_split + test_split : val_split + test_split + train_split],
y_negatives[val_split + test_split : val_split + test_split + train_split],
),
0,
),
)
# Remaining pool of samples are stored separately. These are only labeled as and when required
x_pool_positives, y_pool_positives = (
x_positives[val_split + test_split + train_split :],
y_positives[val_split + test_split + train_split :],
)
x_pool_negatives, y_pool_negatives = (
x_negatives[val_split + test_split + train_split :],
y_negatives[val_split + test_split + train_split :],
)
# Creating TF Datasets for faster prefetching and parallelization
train_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train, y_train))
val_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_val, y_val))
test_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test, y_test))
pool_negatives = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(
(x_pool_negatives, y_pool_negatives)
)
pool_positives = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(
(x_pool_positives, y_pool_positives)
)
print(f"Initial training set size: {len(train_dataset)}")
print(f"Validation set size: {len(val_dataset)}")
print(f"Testing set size: {len(test_dataset)}")
print(f"Unlabeled negative pool: {len(pool_negatives)}")
print(f"Unlabeled positive pool: {len(pool_positives)}")Result
Initial training set size: 15000
Validation set size: 5000
Testing set size: 5000
Unlabeled negative pool: 12500
Unlabeled positive pool: 12500Fitting the TextVectorization layer
Since we are working with text data, we will need to encode the text strings as vectors which would then be passed through an Embedding layer. To make this tokenization process faster, we use the map() function with its parallelization functionality.
vectorizer = layers.TextVectorization(
3000, standardize="lower_and_strip_punctuation", output_sequence_length=150
)
# Adapting the dataset
vectorizer.adapt(
train_dataset.map(lambda x, y: x, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE).batch(256)
)
def vectorize_text(text, label):
text = vectorizer(text)
return text, label
train_dataset = train_dataset.map(
vectorize_text, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE
).prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
pool_negatives = pool_negatives.map(vectorize_text, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
pool_positives = pool_positives.map(vectorize_text, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
val_dataset = val_dataset.batch(256).map(
vectorize_text, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE
)
test_dataset = test_dataset.batch(256).map(
vectorize_text, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.AUTOTUNE
)Creating Helper Functions
# Helper function for merging new history objects with older ones
def append_history(losses, val_losses, accuracy, val_accuracy, history):
losses = losses + history.history["loss"]
val_losses = val_losses + history.history["val_loss"]
accuracy = accuracy + history.history["binary_accuracy"]
val_accuracy = val_accuracy + history.history["val_binary_accuracy"]
return losses, val_losses, accuracy, val_accuracy
# Plotter function
def plot_history(losses, val_losses, accuracies, val_accuracies):
plt.plot(losses)
plt.plot(val_losses)
plt.legend(["train_loss", "val_loss"])
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel("Loss")
plt.show()
plt.plot(accuracies)
plt.plot(val_accuracies)
plt.legend(["train_accuracy", "val_accuracy"])
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel("Accuracy")
plt.show()Creating the Model
We create a small bidirectional LSTM model. When using Active Learning, you should make sure that the model architecture is capable of overfitting to the initial data. Overfitting gives a strong hint that the model will have enough capacity for future, unseen data.
def create_model():
model = keras.models.Sequential(
[
layers.Input(shape=(150,)),
layers.Embedding(input_dim=3000, output_dim=128),
layers.Bidirectional(layers.LSTM(32, return_sequences=True)),
layers.GlobalMaxPool1D(),
layers.Dense(20, activation="relu"),
layers.Dropout(0.5),
layers.Dense(1, activation="sigmoid"),
]
)
model.summary()
return modelTraining on the entire dataset
To show the effectiveness of Active Learning, we will first train the model on the entire dataset containing 40,000 labeled samples. This model will be used for comparison later.
def train_full_model(full_train_dataset, val_dataset, test_dataset):
model = create_model()
model.compile(
loss="binary_crossentropy",
optimizer="rmsprop",
metrics=[
keras.metrics.BinaryAccuracy(),
keras.metrics.FalseNegatives(),
keras.metrics.FalsePositives(),
],
)
# We will save the best model at every epoch and load the best one for evaluation on the test set
history = model.fit(
full_train_dataset.batch(256),
epochs=20,
validation_data=val_dataset,
callbacks=[
keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(patience=4, verbose=1),
keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(
"FullModelCheckpoint.keras", verbose=1, save_best_only=True
),
],
)
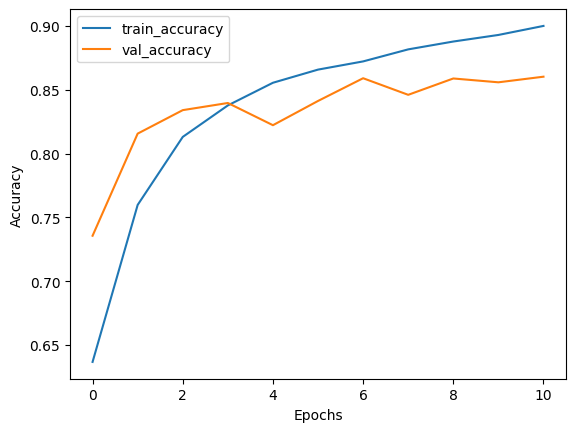
# Plot history
plot_history(
history.history["loss"],
history.history["val_loss"],
history.history["binary_accuracy"],
history.history["val_binary_accuracy"],
)
# Loading the best checkpoint
model = keras.models.load_model("FullModelCheckpoint.keras")
print("-" * 100)
print(
"Test set evaluation: ",
model.evaluate(test_dataset, verbose=0, return_dict=True),
)
print("-" * 100)
return model
# Sampling the full train dataset to train on
full_train_dataset = (
train_dataset.concatenate(pool_positives)
.concatenate(pool_negatives)
.cache()
.shuffle(20000)
)
# Training the full model
full_dataset_model = train_full_model(full_train_dataset, val_dataset, test_dataset)Result
Model: "sequential"
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ Layer (type) ┃ Output Shape ┃ Param # ┃
┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩
│ embedding (Embedding) │ (None, 150, 128) │ 384,000 │
├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤
│ bidirectional (Bidirectional) │ (None, 150, 64) │ 41,216 │
├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤
│ global_max_pooling1d │ (None, 64) │ 0 │
│ (GlobalMaxPooling1D) │ │ │
├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤
│ dense (Dense) │ (None, 20) │ 1,300 │
├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤
│ dropout (Dropout) │ (None, 20) │ 0 │
├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤
│ dense_1 (Dense) │ (None, 1) │ 21 │
└─────────────────────────────────┴────────────────────────┴───────────────┘
Total params: 426,537 (1.63 MB)
Trainable params: 426,537 (1.63 MB)
Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 B)Epoch 1/20
156/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 73ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.6412 - false_negatives: 2084.3333 - false_positives: 5252.1924 - loss: 0.6507
Epoch 1: val_loss improved from inf to 0.57198, saving model to FullModelCheckpoint.keras
157/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 15s 79ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.6411 - false_negatives: 2135.1772 - false_positives: 5292.4053 - loss: 0.6506 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.7356 - val_false_negatives: 898.0000 - val_false_positives: 424.0000 - val_loss: 0.5720
Epoch 2/20
156/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.7448 - false_negatives: 1756.2756 - false_positives: 3249.1411 - loss: 0.5416
Epoch 2: val_loss improved from 0.57198 to 0.41756, saving model to FullModelCheckpoint.keras
157/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 12s 76ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.7450 - false_negatives: 1783.8925 - false_positives: 3279.8101 - loss: 0.5412 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8156 - val_false_negatives: 531.0000 - val_false_positives: 391.0000 - val_loss: 0.4176
Epoch 3/20
156/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8162 - false_negatives: 1539.7693 - false_positives: 2197.1475 - loss: 0.4254
Epoch 3: val_loss improved from 0.41756 to 0.38233, saving model to FullModelCheckpoint.keras
157/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 12s 76ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8161 - false_negatives: 1562.6962 - false_positives: 2221.5886 - loss: 0.4254 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8340 - val_false_negatives: 496.0000 - val_false_positives: 334.0000 - val_loss: 0.3823
Epoch 4/20
156/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8413 - false_negatives: 1400.6538 - false_positives: 1818.7372 - loss: 0.3837
Epoch 4: val_loss improved from 0.38233 to 0.36235, saving model to FullModelCheckpoint.keras
157/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 12s 76ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8412 - false_negatives: 1421.5063 - false_positives: 1839.3102 - loss: 0.3838 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8396 - val_false_negatives: 548.0000 - val_false_positives: 254.0000 - val_loss: 0.3623
Epoch 5/20
156/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8611 - false_negatives: 1264.5256 - false_positives: 1573.5962 - loss: 0.3468
Epoch 5: val_loss did not improve from 0.36235
157/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 12s 75ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8611 - false_negatives: 1283.0632 - false_positives: 1592.3228 - loss: 0.3468 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8222 - val_false_negatives: 734.0000 - val_false_positives: 155.0000 - val_loss: 0.4081
Epoch 6/20
156/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8706 - false_negatives: 1186.9166 - false_positives: 1427.9487 - loss: 0.3301
Epoch 6: val_loss improved from 0.36235 to 0.35041, saving model to FullModelCheckpoint.keras
157/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 12s 76ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8705 - false_negatives: 1204.8038 - false_positives: 1444.9368 - loss: 0.3302 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8412 - val_false_negatives: 569.0000 - val_false_positives: 225.0000 - val_loss: 0.3504
Epoch 7/20
156/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8768 - false_negatives: 1162.4423 - false_positives: 1342.4807 - loss: 0.3084
Epoch 7: val_loss improved from 0.35041 to 0.32680, saving model to FullModelCheckpoint.keras
157/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 12s 76ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8768 - false_negatives: 1179.5253 - false_positives: 1358.4114 - loss: 0.3085 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8590 - val_false_negatives: 364.0000 - val_false_positives: 341.0000 - val_loss: 0.3268
Epoch 8/20
156/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 73ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8865 - false_negatives: 1079.3206 - false_positives: 1250.2693 - loss: 0.2924
Epoch 8: val_loss did not improve from 0.32680
157/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 12s 76ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8864 - false_negatives: 1094.9873 - false_positives: 1265.0632 - loss: 0.2926 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8460 - val_false_negatives: 548.0000 - val_false_positives: 222.0000 - val_loss: 0.3432
Epoch 9/20
156/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 73ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8912 - false_negatives: 1019.1987 - false_positives: 1189.4551 - loss: 0.2807
Epoch 9: val_loss did not improve from 0.32680
157/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 12s 77ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8912 - false_negatives: 1033.9684 - false_positives: 1203.5632 - loss: 0.2808 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8588 - val_false_negatives: 330.0000 - val_false_positives: 376.0000 - val_loss: 0.3302
Epoch 10/20
156/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8997 - false_negatives: 968.6346 - false_positives: 1109.9103 - loss: 0.2669
Epoch 10: val_loss did not improve from 0.32680
157/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 12s 76ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8996 - false_negatives: 983.1202 - false_positives: 1123.3418 - loss: 0.2671 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8558 - val_false_negatives: 445.0000 - val_false_positives: 276.0000 - val_loss: 0.3413
Epoch 11/20
156/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.9055 - false_negatives: 937.0320 - false_positives: 1000.8589 - loss: 0.2520
Epoch 11: val_loss did not improve from 0.32680
157/157 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 12s 76ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.9055 - false_negatives: 950.3608 - false_positives: 1013.6456 - loss: 0.2521 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8602 - val_false_negatives: 402.0000 - val_false_positives: 297.0000 - val_loss: 0.3281
Epoch 11: early stopping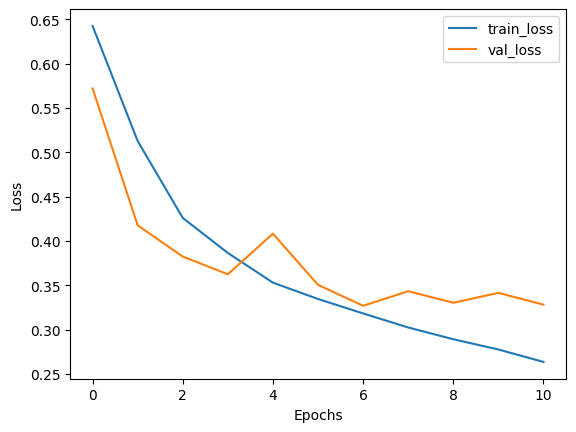
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Test set evaluation: {'binary_accuracy': 0.8507999777793884, 'false_negatives': 397.0, 'false_positives': 349.0, 'loss': 0.3372706174850464}
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Training via Active Learning
The general process we follow when performing Active Learning is demonstrated below:
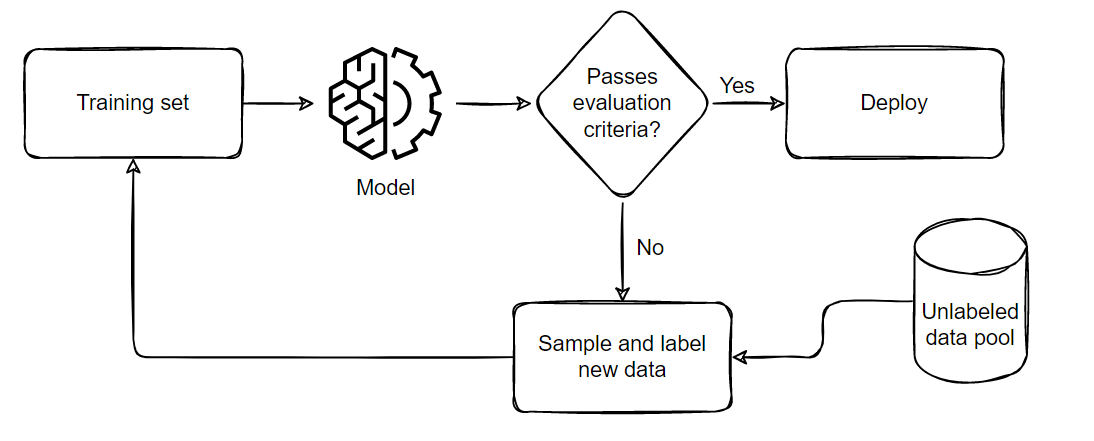
The pipeline can be summarized in five parts:
- Sample and annotate a small, balanced training dataset
- Train the model on this small subset
- Evaluate the model on a balanced testing set
- If the model satisfies the business criteria, deploy it in a real time setting
- If it doesn’t pass the criteria, sample a few more samples according to the ratio of false positives and negatives, add them to the training set and repeat from step 2 till the model passes the tests or till all available data is exhausted.
For the code below, we will perform sampling using the following formula:
$$ \text{Negative Samples} = \frac{\text{False Negatives}}{\text{All False Predictions}} $$
$$ \text{Positive Samples} = \frac{\text{False Positives}}{\text{All False Positives}} $$
Active Learning techniques use callbacks extensively for progress tracking. We will be using model checkpointing and early stopping for this example. The patience parameter for Early Stopping can help minimize overfitting and the time required. We have set it patience=4 for now but since the model is robust, we can increase the patience level if desired.
Note: We are not loading the checkpoint after the first training iteration. In my experience working on Active Learning techniques, this helps the model probe the newly formed loss landscape. Even if the model fails to improve in the second iteration, we will still gain insight about the possible future false positive and negative rates. This will help us sample a better set in the next iteration where the model will have a greater chance to improve.
def train_active_learning_models(
train_dataset,
pool_negatives,
pool_positives,
val_dataset,
test_dataset,
num_iterations=3,
sampling_size=5000,
):
# Creating lists for storing metrics
losses, val_losses, accuracies, val_accuracies = [], [], [], []
model = create_model()
# We will monitor the false positives and false negatives predicted by our model
# These will decide the subsequent sampling ratio for every Active Learning loop
model.compile(
loss="binary_crossentropy",
optimizer="rmsprop",
metrics=[
keras.metrics.BinaryAccuracy(),
keras.metrics.FalseNegatives(),
keras.metrics.FalsePositives(),
],
)
# Defining checkpoints.
# The checkpoint callback is reused throughout the training since it only saves the best overall model.
checkpoint = keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(
"AL_Model.keras", save_best_only=True, verbose=1
)
# Here, patience is set to 4. This can be set higher if desired.
early_stopping = keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(patience=4, verbose=1)
print(f"Starting to train with {len(train_dataset)} samples")
# Initial fit with a small subset of the training set
history = model.fit(
train_dataset.cache().shuffle(20000).batch(256),
epochs=20,
validation_data=val_dataset,
callbacks=[checkpoint, early_stopping],
)
# Appending history
losses, val_losses, accuracies, val_accuracies = append_history(
losses, val_losses, accuracies, val_accuracies, history
)
for iteration in range(num_iterations):
# Getting predictions from previously trained model
predictions = model.predict(test_dataset)
# Generating labels from the output probabilities
rounded = ops.where(ops.greater(predictions, 0.5), 1, 0)
# Evaluating the number of zeros and ones incorrrectly classified
_, _, false_negatives, false_positives = model.evaluate(test_dataset, verbose=0)
print("-" * 100)
print(
f"Number of zeros incorrectly classified: {false_negatives}, Number of ones incorrectly classified: {false_positives}"
)
# This technique of Active Learning demonstrates ratio based sampling where
# Number of ones/zeros to sample = Number of ones/zeros incorrectly classified / Total incorrectly classified
if false_negatives != 0 and false_positives != 0:
total = false_negatives + false_positives
sample_ratio_ones, sample_ratio_zeros = (
false_positives / total,
false_negatives / total,
)
# In the case where all samples are correctly predicted, we can sample both classes equally
else:
sample_ratio_ones, sample_ratio_zeros = 0.5, 0.5
print(
f"Sample ratio for positives: {sample_ratio_ones}, Sample ratio for negatives:{sample_ratio_zeros}"
)
# Sample the required number of ones and zeros
sampled_dataset = pool_negatives.take(
int(sample_ratio_zeros * sampling_size)
).concatenate(pool_positives.take(int(sample_ratio_ones * sampling_size)))
# Skip the sampled data points to avoid repetition of sample
pool_negatives = pool_negatives.skip(int(sample_ratio_zeros * sampling_size))
pool_positives = pool_positives.skip(int(sample_ratio_ones * sampling_size))
# Concatenating the train_dataset with the sampled_dataset
train_dataset = train_dataset.concatenate(sampled_dataset).prefetch(
tf.data.AUTOTUNE
)
print(f"Starting training with {len(train_dataset)} samples")
print("-" * 100)
# We recompile the model to reset the optimizer states and retrain the model
model.compile(
loss="binary_crossentropy",
optimizer="rmsprop",
metrics=[
keras.metrics.BinaryAccuracy(),
keras.metrics.FalseNegatives(),
keras.metrics.FalsePositives(),
],
)
history = model.fit(
train_dataset.cache().shuffle(20000).batch(256),
validation_data=val_dataset,
epochs=20,
callbacks=[
checkpoint,
keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(patience=4, verbose=1),
],
)
# Appending the history
losses, val_losses, accuracies, val_accuracies = append_history(
losses, val_losses, accuracies, val_accuracies, history
)
# Loading the best model from this training loop
model = keras.models.load_model("AL_Model.keras")
# Plotting the overall history and evaluating the final model
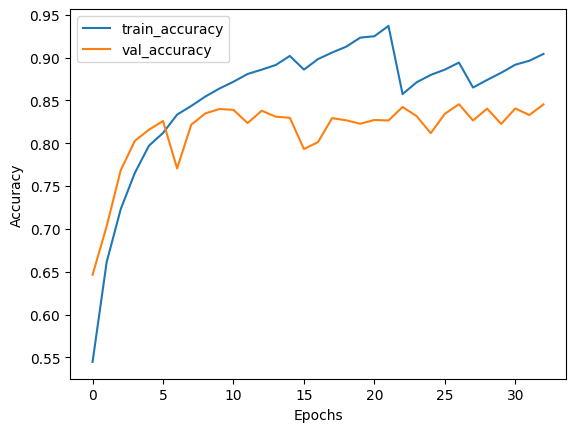
plot_history(losses, val_losses, accuracies, val_accuracies)
print("-" * 100)
print(
"Test set evaluation: ",
model.evaluate(test_dataset, verbose=0, return_dict=True),
)
print("-" * 100)
return model
active_learning_model = train_active_learning_models(
train_dataset, pool_negatives, pool_positives, val_dataset, test_dataset
)Result
Model: "sequential_1"
┏━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┳━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┓
┃ Layer (type) ┃ Output Shape ┃ Param # ┃
┡━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━╇━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━┩
│ embedding_1 (Embedding) │ (None, 150, 128) │ 384,000 │
├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤
│ bidirectional_1 (Bidirectional) │ (None, 150, 64) │ 41,216 │
├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤
│ global_max_pooling1d_1 │ (None, 64) │ 0 │
│ (GlobalMaxPooling1D) │ │ │
├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤
│ dense_2 (Dense) │ (None, 20) │ 1,300 │
├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤
│ dropout_1 (Dropout) │ (None, 20) │ 0 │
├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────┼───────────────┤
│ dense_3 (Dense) │ (None, 1) │ 21 │
└─────────────────────────────────┴────────────────────────┴───────────────┘
Total params: 426,537 (1.63 MB)
Trainable params: 426,537 (1.63 MB)
Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 B)Starting to train with 15000 samples
Epoch 1/20
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.5197 - false_negatives_1: 1686.7457 - false_positives_1: 1938.3051 - loss: 0.6918
Epoch 1: val_loss improved from inf to 0.67428, saving model to AL_Model.keras
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 8s 89ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.5202 - false_negatives_1: 1716.9833 - false_positives_1: 1961.4667 - loss: 0.6917 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.6464 - val_false_negatives_1: 279.0000 - val_false_positives_1: 1489.0000 - val_loss: 0.6743
Epoch 2/20
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.6505 - false_negatives_1: 1216.0170 - false_positives_1: 1434.2373 - loss: 0.6561
Epoch 2: val_loss improved from 0.67428 to 0.59133, saving model to AL_Model.keras
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 5s 83ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.6507 - false_negatives_1: 1234.9833 - false_positives_1: 1455.7667 - loss: 0.6558 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.7032 - val_false_negatives_1: 235.0000 - val_false_positives_1: 1249.0000 - val_loss: 0.5913
Epoch 3/20
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.7103 - false_negatives_1: 939.5255 - false_positives_1: 1235.8983 - loss: 0.5829
Epoch 3: val_loss improved from 0.59133 to 0.51602, saving model to AL_Model.keras
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 5s 83ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.7106 - false_negatives_1: 953.0500 - false_positives_1: 1255.3167 - loss: 0.5827 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.7686 - val_false_negatives_1: 812.0000 - val_false_positives_1: 345.0000 - val_loss: 0.5160
Epoch 4/20
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.7545 - false_negatives_1: 787.4237 - false_positives_1: 1070.0339 - loss: 0.5214
Epoch 4: val_loss improved from 0.51602 to 0.43948, saving model to AL_Model.keras
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 5s 83ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.7547 - false_negatives_1: 799.2667 - false_positives_1: 1085.8833 - loss: 0.5212 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8028 - val_false_negatives_1: 342.0000 - val_false_positives_1: 644.0000 - val_loss: 0.4395
Epoch 5/20
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.7919 - false_negatives_1: 676.7458 - false_positives_1: 907.4915 - loss: 0.4657
Epoch 5: val_loss improved from 0.43948 to 0.41679, saving model to AL_Model.keras
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 5s 83ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.7920 - false_negatives_1: 687.3834 - false_positives_1: 921.1667 - loss: 0.4655 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8158 - val_false_negatives_1: 598.0000 - val_false_positives_1: 323.0000 - val_loss: 0.4168
Epoch 6/20
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.7994 - false_negatives_1: 661.3560 - false_positives_1: 828.0847 - loss: 0.4498
Epoch 6: val_loss improved from 0.41679 to 0.39680, saving model to AL_Model.keras
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 5s 83ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.7997 - false_negatives_1: 671.3666 - false_positives_1: 840.2500 - loss: 0.4495 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8260 - val_false_negatives_1: 382.0000 - val_false_positives_1: 488.0000 - val_loss: 0.3968
Epoch 7/20
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8311 - false_negatives_1: 589.1187 - false_positives_1: 707.0170 - loss: 0.4017
Epoch 7: val_loss did not improve from 0.39680
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 5s 83ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8312 - false_negatives_1: 598.3500 - false_positives_1: 717.8167 - loss: 0.4016 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.7706 - val_false_negatives_1: 1004.0000 - val_false_positives_1: 143.0000 - val_loss: 0.4884
Epoch 8/20
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8365 - false_negatives_1: 566.7288 - false_positives_1: 649.9322 - loss: 0.3896
Epoch 8: val_loss did not improve from 0.39680
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 5s 83ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8366 - false_negatives_1: 575.2833 - false_positives_1: 660.2167 - loss: 0.3895 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8216 - val_false_negatives_1: 623.0000 - val_false_positives_1: 269.0000 - val_loss: 0.4043
Epoch 9/20
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8531 - false_negatives_1: 519.0170 - false_positives_1: 591.6440 - loss: 0.3631
Epoch 9: val_loss improved from 0.39680 to 0.37727, saving model to AL_Model.keras
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 5s 83ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8531 - false_negatives_1: 527.2667 - false_positives_1: 601.2500 - loss: 0.3631 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8348 - val_false_negatives_1: 296.0000 - val_false_positives_1: 530.0000 - val_loss: 0.3773
Epoch 10/20
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8686 - false_negatives_1: 475.7966 - false_positives_1: 569.0508 - loss: 0.3387
Epoch 10: val_loss improved from 0.37727 to 0.37354, saving model to AL_Model.keras
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 5s 83ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8685 - false_negatives_1: 483.5000 - false_positives_1: 577.9667 - loss: 0.3387 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8400 - val_false_negatives_1: 327.0000 - val_false_positives_1: 473.0000 - val_loss: 0.3735
Epoch 11/20
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8716 - false_negatives_1: 452.1356 - false_positives_1: 522.1187 - loss: 0.3303
Epoch 11: val_loss improved from 0.37354 to 0.37074, saving model to AL_Model.keras
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 5s 83ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8716 - false_negatives_1: 459.3833 - false_positives_1: 530.6667 - loss: 0.3303 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8390 - val_false_negatives_1: 362.0000 - val_false_positives_1: 443.0000 - val_loss: 0.3707
Epoch 12/20
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8833 - false_negatives_1: 433.0678 - false_positives_1: 481.1864 - loss: 0.3065
Epoch 12: val_loss did not improve from 0.37074
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 5s 83ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8833 - false_negatives_1: 439.8333 - false_positives_1: 488.9667 - loss: 0.3066 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8236 - val_false_negatives_1: 208.0000 - val_false_positives_1: 674.0000 - val_loss: 0.4046
Epoch 13/20
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8876 - false_negatives_1: 384.8305 - false_positives_1: 476.5254 - loss: 0.2978
Epoch 13: val_loss did not improve from 0.37074
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 5s 82ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8876 - false_negatives_1: 391.2667 - false_positives_1: 484.2500 - loss: 0.2978 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8380 - val_false_negatives_1: 364.0000 - val_false_positives_1: 446.0000 - val_loss: 0.3783
Epoch 14/20
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8976 - false_negatives_1: 378.0169 - false_positives_1: 433.9831 - loss: 0.2754
Epoch 14: val_loss did not improve from 0.37074
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 5s 83ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8975 - false_negatives_1: 384.2333 - false_positives_1: 441.3833 - loss: 0.2757 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8310 - val_false_negatives_1: 525.0000 - val_false_positives_1: 320.0000 - val_loss: 0.3957
Epoch 15/20
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.9013 - false_negatives_1: 354.9322 - false_positives_1: 403.1695 - loss: 0.2709
Epoch 15: val_loss did not improve from 0.37074
59/59 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 5s 83ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.9013 - false_negatives_1: 360.4000 - false_positives_1: 409.5833 - loss: 0.2709 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8298 - val_false_negatives_1: 302.0000 - val_false_positives_1: 549.0000 - val_loss: 0.4015
Epoch 15: early stopping
20/20 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 39ms/step
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number of zeros incorrectly classified: 290.0, Number of ones incorrectly classified: 538.0
Sample ratio for positives: 0.6497584541062802, Sample ratio for negatives:0.3502415458937198
Starting training with 19999 samples
----------------------------------------------------------------------------Epoch 1/20
78/79 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8735 - false_negatives_2: 547.2436 - false_positives_2: 650.2436 - loss: 0.3527
Epoch 1: val_loss did not improve from 0.37074
79/79 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 9s 84ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8738 - false_negatives_2: 559.2125 - false_positives_2: 665.3375 - loss: 0.3518 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.7932 - val_false_negatives_2: 119.0000 - val_false_positives_2: 915.0000 - val_loss: 0.4949
Epoch 2/20
78/79 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8961 - false_negatives_2: 470.2436 - false_positives_2: 576.1539 - loss: 0.2824
Epoch 2: val_loss did not improve from 0.37074
79/79 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 6s 80ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8962 - false_negatives_2: 481.4125 - false_positives_2: 589.6750 - loss: 0.2823 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8014 - val_false_negatives_2: 809.0000 - val_false_positives_2: 184.0000 - val_loss: 0.4580
Epoch 3/20
78/79 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.9059 - false_negatives_2: 442.2051 - false_positives_2: 500.5385 - loss: 0.2628
Epoch 3: val_loss did not improve from 0.37074
79/79 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 6s 80ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.9059 - false_negatives_2: 452.6750 - false_positives_2: 513.5250 - loss: 0.2629 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8294 - val_false_negatives_2: 302.0000 - val_false_positives_2: 551.0000 - val_loss: 0.3868
Epoch 4/20
78/79 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.9188 - false_negatives_2: 394.5513 - false_positives_2: 462.4359 - loss: 0.2391
Epoch 4: val_loss did not improve from 0.37074
79/79 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 6s 80ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.9187 - false_negatives_2: 405.0625 - false_positives_2: 474.1250 - loss: 0.2393 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8268 - val_false_negatives_2: 225.0000 - val_false_positives_2: 641.0000 - val_loss: 0.4197
Epoch 5/20
78/79 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.9255 - false_negatives_2: 349.8718 - false_positives_2: 413.0898 - loss: 0.2270
Epoch 5: val_loss did not improve from 0.37074
79/79 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 6s 79ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.9254 - false_negatives_2: 358.6500 - false_positives_2: 423.5625 - loss: 0.2270 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8228 - val_false_negatives_2: 611.0000 - val_false_positives_2: 275.0000 - val_loss: 0.4233
Epoch 6/20
78/79 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 73ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.9265 - false_negatives_2: 349.8590 - false_positives_2: 389.9359 - loss: 0.2147
Epoch 6: val_loss did not improve from 0.37074
79/79 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 6s 80ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.9265 - false_negatives_2: 358.8375 - false_positives_2: 399.9875 - loss: 0.2148 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8272 - val_false_negatives_2: 581.0000 - val_false_positives_2: 283.0000 - val_loss: 0.4415
Epoch 7/20
78/79 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.9409 - false_negatives_2: 286.7820 - false_positives_2: 322.7949 - loss: 0.1877
Epoch 7: val_loss did not improve from 0.37074
79/79 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 6s 79ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.9408 - false_negatives_2: 294.4375 - false_positives_2: 331.4000 - loss: 0.1880 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8266 - val_false_negatives_2: 528.0000 - val_false_positives_2: 339.0000 - val_loss: 0.4419
Epoch 7: early stopping
20/20 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 39ms/step
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number of zeros incorrectly classified: 376.0, Number of ones incorrectly classified: 442.0
Sample ratio for positives: 0.5403422982885085, Sample ratio for negatives:0.45965770171149145
Starting training with 24998 samples
------------------------------------------------------------------------------Epoch 1/20
98/98 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 73ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8509 - false_negatives_3: 809.9184 - false_positives_3: 1018.9286 - loss: 0.3732
Epoch 1: val_loss improved from 0.37074 to 0.36196, saving model to AL_Model.keras
98/98 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 11s 83ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8509 - false_negatives_3: 817.5757 - false_positives_3: 1028.7980 - loss: 0.3731 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8424 - val_false_negatives_3: 368.0000 - val_false_positives_3: 420.0000 - val_loss: 0.3620
Epoch 2/20
98/98 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8744 - false_negatives_3: 734.7449 - false_positives_3: 884.7755 - loss: 0.3185
Epoch 2: val_loss did not improve from 0.36196
98/98 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 8s 79ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8744 - false_negatives_3: 741.9697 - false_positives_3: 893.7172 - loss: 0.3186 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8316 - val_false_negatives_3: 202.0000 - val_false_positives_3: 640.0000 - val_loss: 0.3792
Epoch 3/20
98/98 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8830 - false_negatives_3: 684.1326 - false_positives_3: 807.8878 - loss: 0.3090
Epoch 3: val_loss did not improve from 0.36196
98/98 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 8s 79ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8830 - false_negatives_3: 691.0707 - false_positives_3: 816.2222 - loss: 0.3090 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8118 - val_false_negatives_3: 738.0000 - val_false_positives_3: 203.0000 - val_loss: 0.4112
Epoch 4/20
98/98 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8892 - false_negatives_3: 651.9898 - false_positives_3: 776.4388 - loss: 0.2928
Epoch 4: val_loss did not improve from 0.36196
98/98 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 8s 79ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8892 - false_negatives_3: 658.4041 - false_positives_3: 784.3839 - loss: 0.2928 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8344 - val_false_negatives_3: 557.0000 - val_false_positives_3: 271.0000 - val_loss: 0.3734
Epoch 5/20
98/98 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 72ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8975 - false_negatives_3: 612.0714 - false_positives_3: 688.9184 - loss: 0.2806
Epoch 5: val_loss did not improve from 0.36196
98/98 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 8s 79ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8974 - false_negatives_3: 618.4343 - false_positives_3: 696.1313 - loss: 0.2807 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8456 - val_false_negatives_3: 446.0000 - val_false_positives_3: 326.0000 - val_loss: 0.3658
Epoch 5: early stopping
20/20 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 40ms/step
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Number of zeros incorrectly classified: 407.0, Number of ones incorrectly classified: 410.0
Sample ratio for positives: 0.5018359853121175, Sample ratio for negatives:0.4981640146878825
Starting training with 29997 samples
------------------------------------------------------------------------------Epoch 1/20
117/118 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 76ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8621 - false_negatives_4: 916.2393 - false_positives_4: 1130.9744 - loss: 0.3527
Epoch 1: val_loss did not improve from 0.36196
118/118 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 13s 85ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8621 - false_negatives_4: 931.0924 - false_positives_4: 1149.7479 - loss: 0.3525 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8266 - val_false_negatives_4: 627.0000 - val_false_positives_4: 240.0000 - val_loss: 0.3802
Epoch 2/20
117/118 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 76ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8761 - false_negatives_4: 876.4872 - false_positives_4: 1005.5726 - loss: 0.3195
Epoch 2: val_loss improved from 0.36196 to 0.35707, saving model to AL_Model.keras
118/118 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 82ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8760 - false_negatives_4: 891.0504 - false_positives_4: 1022.9412 - loss: 0.3196 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8404 - val_false_negatives_4: 479.0000 - val_false_positives_4: 319.0000 - val_loss: 0.3571
Epoch 3/20
117/118 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 74ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8874 - false_negatives_4: 801.1710 - false_positives_4: 941.4786 - loss: 0.2965
Epoch 3: val_loss did not improve from 0.35707
118/118 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 9s 79ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8873 - false_negatives_4: 814.8319 - false_positives_4: 957.8571 - loss: 0.2966 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8226 - val_false_negatives_4: 677.0000 - val_false_positives_4: 210.0000 - val_loss: 0.3948
Epoch 4/20
117/118 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 76ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8977 - false_negatives_4: 740.5385 - false_positives_4: 837.1710 - loss: 0.2768
Epoch 4: val_loss did not improve from 0.35707
118/118 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 81ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.8976 - false_negatives_4: 753.5378 - false_positives_4: 852.2437 - loss: 0.2770 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8406 - val_false_negatives_4: 530.0000 - val_false_positives_4: 267.0000 - val_loss: 0.3630
Epoch 5/20
117/118 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 76ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.9020 - false_negatives_4: 722.5214 - false_positives_4: 808.2308 - loss: 0.2674
Epoch 5: val_loss did not improve from 0.35707
118/118 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 82ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.9019 - false_negatives_4: 734.8655 - false_positives_4: 822.4117 - loss: 0.2676 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8330 - val_false_negatives_4: 592.0000 - val_false_positives_4: 243.0000 - val_loss: 0.3805
Epoch 6/20
117/118 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━[37m━ 0s 76ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.9059 - false_negatives_4: 682.1453 - false_positives_4: 737.0513 - loss: 0.2525
Epoch 6: val_loss did not improve from 0.35707
118/118 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 82ms/step - binary_accuracy: 0.9059 - false_negatives_4: 693.6387 - false_positives_4: 749.9412 - loss: 0.2526 - val_binary_accuracy: 0.8454 - val_false_negatives_4: 391.0000 - val_false_positives_4: 382.0000 - val_loss: 0.3620
Epoch 6: early stopping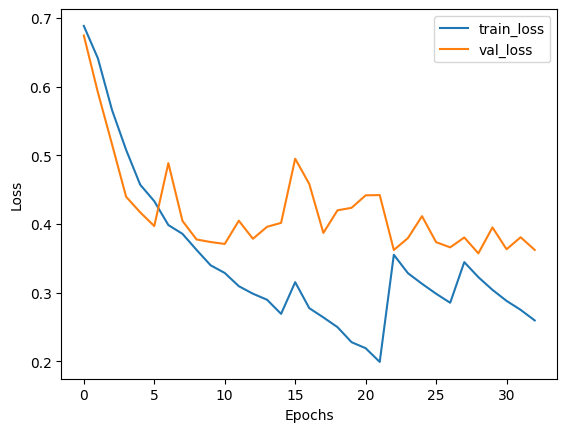
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Test set evaluation: {'binary_accuracy': 0.8424000144004822, 'false_negatives_4': 491.0, 'false_positives_4': 297.0, 'loss': 0.3661557137966156}
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Conclusion
Active Learning is a growing area of research. This example demonstrates the cost-efficiency benefits of using Active Learning, as it eliminates the need to annotate large amounts of data, saving resources.
The following are some noteworthy observations from this example:
- We only require 30,000 samples to reach the same (if not better) scores as the model trained on the full dataset. This means that in a real life setting, we save the effort required for annotating 10,000 images!
- The number of false negatives and false positives are well balanced at the end of the training as compared to the skewed ratio obtained from the full training. This makes the model slightly more useful in real life scenarios where both the labels hold equal importance.
For further reading about the types of sampling ratios, training techniques or available open source libraries/implementations, you can refer to the resources below:
- Active Learning Literature Survey (Burr Settles, 2010).
- modAL: A Modular Active Learning framework.
- Google’s unofficial Active Learning playground.