Conditional GAN
- Original Link : https://keras.io/examples/generative/conditional_gan/
- Last Checked at : 2024-11-23
Author: Sayak Paul
Date created: 2021/07/13
Last modified: 2024/01/02
Description: Training a GAN conditioned on class labels to generate handwritten digits.
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) let us generate novel image data, video data, or audio data from a random input. Typically, the random input is sampled from a normal distribution, before going through a series of transformations that turn it into something plausible (image, video, audio, etc.).
However, a simple DCGAN doesn’t let us control the appearance (e.g. class) of the samples we’re generating. For instance, with a GAN that generates MNIST handwritten digits, a simple DCGAN wouldn’t let us choose the class of digits we’re generating. To be able to control what we generate, we need to condition the GAN output on a semantic input, such as the class of an image.
In this example, we’ll build a Conditional GAN that can generate MNIST handwritten digits conditioned on a given class. Such a model can have various useful applications:
- let’s say you are dealing with an imbalanced image dataset, and you’d like to gather more examples for the skewed class to balance the dataset. Data collection can be a costly process on its own. You could instead train a Conditional GAN and use it to generate novel images for the class that needs balancing.
- Since the generator learns to associate the generated samples with the class labels, its representations can also be used for other downstream tasks.
Following are the references used for developing this example:
If you need a refresher on GANs, you can refer to the “Generative adversarial networks” section of this resource.
This example requires TensorFlow 2.5 or higher, as well as TensorFlow Docs, which can be installed using the following command:
!pip install -q git+https://github.com/tensorflow/docsImports
import keras
from keras import layers
from keras import ops
from tensorflow_docs.vis import embed
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import imageioConstants and hyperparameters
batch_size = 64
num_channels = 1
num_classes = 10
image_size = 28
latent_dim = 128Loading the MNIST dataset and preprocessing it
# We'll use all the available examples from both the training and test
# sets.
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
all_digits = np.concatenate([x_train, x_test])
all_labels = np.concatenate([y_train, y_test])
# Scale the pixel values to [0, 1] range, add a channel dimension to
# the images, and one-hot encode the labels.
all_digits = all_digits.astype("float32") / 255.0
all_digits = np.reshape(all_digits, (-1, 28, 28, 1))
all_labels = keras.utils.to_categorical(all_labels, 10)
# Create tf.data.Dataset.
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((all_digits, all_labels))
dataset = dataset.shuffle(buffer_size=1024).batch(batch_size)
print(f"Shape of training images: {all_digits.shape}")
print(f"Shape of training labels: {all_labels.shape}")Result
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/tf-keras-datasets/mnist.npz
11490434/11490434 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 0us/step
Shape of training images: (70000, 28, 28, 1)
Shape of training labels: (70000, 10)Calculating the number of input channel for the generator and discriminator
In a regular (unconditional) GAN, we start by sampling noise (of some fixed dimension) from a normal distribution. In our case, we also need to account for the class labels. We will have to add the number of classes to the input channels of the generator (noise input) as well as the discriminator (generated image input).
generator_in_channels = latent_dim + num_classes
discriminator_in_channels = num_channels + num_classes
print(generator_in_channels, discriminator_in_channels)Result
138 11Creating the discriminator and generator
The model definitions (discriminator, generator, and ConditionalGAN) have been adapted from this example.
# Create the discriminator.
discriminator = keras.Sequential(
[
keras.layers.InputLayer((28, 28, discriminator_in_channels)),
layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), strides=(2, 2), padding="same"),
layers.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2),
layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), strides=(2, 2), padding="same"),
layers.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2),
layers.GlobalMaxPooling2D(),
layers.Dense(1),
],
name="discriminator",
)
# Create the generator.
generator = keras.Sequential(
[
keras.layers.InputLayer((generator_in_channels,)),
# We want to generate 128 + num_classes coefficients to reshape into a
# 7x7x(128 + num_classes) map.
layers.Dense(7 * 7 * generator_in_channels),
layers.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2),
layers.Reshape((7, 7, generator_in_channels)),
layers.Conv2DTranspose(128, (4, 4), strides=(2, 2), padding="same"),
layers.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2),
layers.Conv2DTranspose(128, (4, 4), strides=(2, 2), padding="same"),
layers.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2),
layers.Conv2D(1, (7, 7), padding="same", activation="sigmoid"),
],
name="generator",
)Creating a ConditionalGAN model
class ConditionalGAN(keras.Model):
def __init__(self, discriminator, generator, latent_dim):
super().__init__()
self.discriminator = discriminator
self.generator = generator
self.latent_dim = latent_dim
self.seed_generator = keras.random.SeedGenerator(1337)
self.gen_loss_tracker = keras.metrics.Mean(name="generator_loss")
self.disc_loss_tracker = keras.metrics.Mean(name="discriminator_loss")
@property
def metrics(self):
return [self.gen_loss_tracker, self.disc_loss_tracker]
def compile(self, d_optimizer, g_optimizer, loss_fn):
super().compile()
self.d_optimizer = d_optimizer
self.g_optimizer = g_optimizer
self.loss_fn = loss_fn
def train_step(self, data):
# Unpack the data.
real_images, one_hot_labels = data
# Add dummy dimensions to the labels so that they can be concatenated with
# the images. This is for the discriminator.
image_one_hot_labels = one_hot_labels[:, :, None, None]
image_one_hot_labels = ops.repeat(
image_one_hot_labels, repeats=[image_size * image_size]
)
image_one_hot_labels = ops.reshape(
image_one_hot_labels, (-1, image_size, image_size, num_classes)
)
# Sample random points in the latent space and concatenate the labels.
# This is for the generator.
batch_size = ops.shape(real_images)[0]
random_latent_vectors = keras.random.normal(
shape=(batch_size, self.latent_dim), seed=self.seed_generator
)
random_vector_labels = ops.concatenate(
[random_latent_vectors, one_hot_labels], axis=1
)
# Decode the noise (guided by labels) to fake images.
generated_images = self.generator(random_vector_labels)
# Combine them with real images. Note that we are concatenating the labels
# with these images here.
fake_image_and_labels = ops.concatenate(
[generated_images, image_one_hot_labels], -1
)
real_image_and_labels = ops.concatenate([real_images, image_one_hot_labels], -1)
combined_images = ops.concatenate(
[fake_image_and_labels, real_image_and_labels], axis=0
)
# Assemble labels discriminating real from fake images.
labels = ops.concatenate(
[ops.ones((batch_size, 1)), ops.zeros((batch_size, 1))], axis=0
)
# Train the discriminator.
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
predictions = self.discriminator(combined_images)
d_loss = self.loss_fn(labels, predictions)
grads = tape.gradient(d_loss, self.discriminator.trainable_weights)
self.d_optimizer.apply_gradients(
zip(grads, self.discriminator.trainable_weights)
)
# Sample random points in the latent space.
random_latent_vectors = keras.random.normal(
shape=(batch_size, self.latent_dim), seed=self.seed_generator
)
random_vector_labels = ops.concatenate(
[random_latent_vectors, one_hot_labels], axis=1
)
# Assemble labels that say "all real images".
misleading_labels = ops.zeros((batch_size, 1))
# Train the generator (note that we should *not* update the weights
# of the discriminator)!
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
fake_images = self.generator(random_vector_labels)
fake_image_and_labels = ops.concatenate(
[fake_images, image_one_hot_labels], -1
)
predictions = self.discriminator(fake_image_and_labels)
g_loss = self.loss_fn(misleading_labels, predictions)
grads = tape.gradient(g_loss, self.generator.trainable_weights)
self.g_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, self.generator.trainable_weights))
# Monitor loss.
self.gen_loss_tracker.update_state(g_loss)
self.disc_loss_tracker.update_state(d_loss)
return {
"g_loss": self.gen_loss_tracker.result(),
"d_loss": self.disc_loss_tracker.result(),
}Training the Conditional GAN
cond_gan = ConditionalGAN(
discriminator=discriminator, generator=generator, latent_dim=latent_dim
)
cond_gan.compile(
d_optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.0003),
g_optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.0003),
loss_fn=keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
)
cond_gan.fit(dataset, epochs=20)Result
Epoch 1/20
18/1094 [37m━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.6321 - g_loss: 0.7887
WARNING: All log messages before absl::InitializeLog() is called are written to STDERR
I0000 00:00:1704233262.157522 6737 device_compiler.h:186] Compiled cluster using XLA! This line is logged at most once for the lifetime of the process.
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 24s 14ms/step - d_loss: 0.4052 - g_loss: 1.5851 - discriminator_loss: 0.4390 - generator_loss: 1.4775
Epoch 2/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.5116 - g_loss: 1.2740 - discriminator_loss: 0.4872 - generator_loss: 1.3330
Epoch 3/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.3626 - g_loss: 1.6775 - discriminator_loss: 0.3252 - generator_loss: 1.8219
Epoch 4/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.2248 - g_loss: 2.2898 - discriminator_loss: 0.3418 - generator_loss: 2.0042
Epoch 5/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.6017 - g_loss: 1.0428 - discriminator_loss: 0.6076 - generator_loss: 1.0176
Epoch 6/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.6395 - g_loss: 0.9258 - discriminator_loss: 0.6448 - generator_loss: 0.9134
Epoch 7/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.6402 - g_loss: 0.8914 - discriminator_loss: 0.6458 - generator_loss: 0.8773
Epoch 8/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.6549 - g_loss: 0.8440 - discriminator_loss: 0.6555 - generator_loss: 0.8364
Epoch 9/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.6603 - g_loss: 0.8316 - discriminator_loss: 0.6606 - generator_loss: 0.8241
Epoch 10/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.6594 - g_loss: 0.8169 - discriminator_loss: 0.6605 - generator_loss: 0.8218
Epoch 11/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.6719 - g_loss: 0.7979 - discriminator_loss: 0.6649 - generator_loss: 0.8096
Epoch 12/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.6641 - g_loss: 0.7992 - discriminator_loss: 0.6621 - generator_loss: 0.7953
Epoch 13/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.6657 - g_loss: 0.7979 - discriminator_loss: 0.6624 - generator_loss: 0.7924
Epoch 14/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.6586 - g_loss: 0.8220 - discriminator_loss: 0.6566 - generator_loss: 0.8174
Epoch 15/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.6646 - g_loss: 0.7916 - discriminator_loss: 0.6578 - generator_loss: 0.7973
Epoch 16/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.6624 - g_loss: 0.7911 - discriminator_loss: 0.6587 - generator_loss: 0.7966
Epoch 17/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.6586 - g_loss: 0.8060 - discriminator_loss: 0.6550 - generator_loss: 0.7997
Epoch 18/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.6526 - g_loss: 0.7946 - discriminator_loss: 0.6523 - generator_loss: 0.7948
Epoch 19/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.6525 - g_loss: 0.8039 - discriminator_loss: 0.6497 - generator_loss: 0.8066
Epoch 20/20
1094/1094 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 10s 9ms/step - d_loss: 0.6480 - g_loss: 0.8005 - discriminator_loss: 0.6469 - generator_loss: 0.8022
<keras.src.callbacks.history.History at 0x7f541a1b5f90>Interpolating between classes with the trained generator
# We first extract the trained generator from our Conditional GAN.
trained_gen = cond_gan.generator
# Choose the number of intermediate images that would be generated in
# between the interpolation + 2 (start and last images).
num_interpolation = 9 # @param {type:"integer"}
# Sample noise for the interpolation.
interpolation_noise = keras.random.normal(shape=(1, latent_dim))
interpolation_noise = ops.repeat(interpolation_noise, repeats=num_interpolation)
interpolation_noise = ops.reshape(interpolation_noise, (num_interpolation, latent_dim))
def interpolate_class(first_number, second_number):
# Convert the start and end labels to one-hot encoded vectors.
first_label = keras.utils.to_categorical([first_number], num_classes)
second_label = keras.utils.to_categorical([second_number], num_classes)
first_label = ops.cast(first_label, "float32")
second_label = ops.cast(second_label, "float32")
# Calculate the interpolation vector between the two labels.
percent_second_label = ops.linspace(0, 1, num_interpolation)[:, None]
percent_second_label = ops.cast(percent_second_label, "float32")
interpolation_labels = (
first_label * (1 - percent_second_label) + second_label * percent_second_label
)
# Combine the noise and the labels and run inference with the generator.
noise_and_labels = ops.concatenate([interpolation_noise, interpolation_labels], 1)
fake = trained_gen.predict(noise_and_labels)
return fake
start_class = 2 # @param {type:"slider", min:0, max:9, step:1}
end_class = 6 # @param {type:"slider", min:0, max:9, step:1}
fake_images = interpolate_class(start_class, end_class)Result
1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 427ms/stepHere, we first sample noise from a normal distribution and then we repeat that for num_interpolation times and reshape the result accordingly. We then distribute it uniformly for num_interpolation with the label identities being present in some proportion.
fake_images *= 255.0
converted_images = fake_images.astype(np.uint8)
converted_images = ops.image.resize(converted_images, (96, 96)).numpy().astype(np.uint8)
imageio.mimsave("animation.gif", converted_images[:, :, :, 0], fps=1)
embed.embed_file("animation.gif")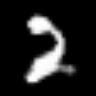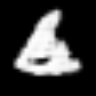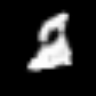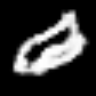
We can further improve the performance of this model with recipes like WGAN-GP. Conditional generation is also widely used in many modern image generation architectures like VQ-GANs, DALL-E, etc.
You can use the trained model hosted on Hugging Face Hub and try the demo on Hugging Face Spaces.